| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Polyethylene-polypropylene glycol
CAS:9003-11-6 |
|
 |
poly(ethylene glycol-co-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether
CAS:9038-95-3 |
|
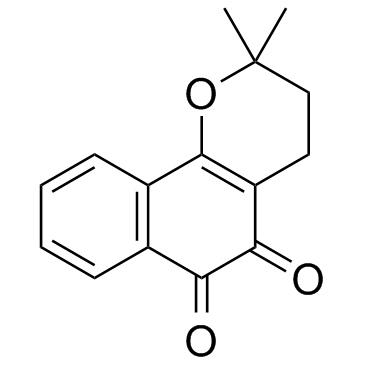 |
Beta-Lapachone
CAS:4707-32-8 |