| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
quizalofop-P-ethyl
CAS:100646-51-3 |
|
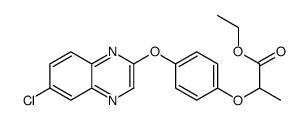 |
quizalofop-ethyl
CAS:76578-14-8 |