| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
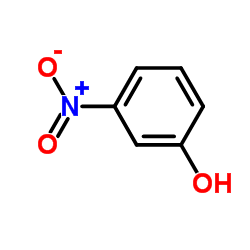 |
3-Nitrophenol
CAS:554-84-7 |
|
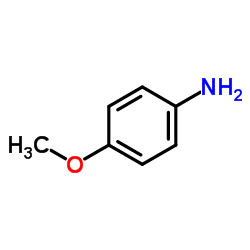 |
p-Anisidine
CAS:104-94-9 |