Reductive degradation of nitrobenzene in aqueous solution by zero-valent iron.
Yang Mu, Han-Qing Yu, Jia-Chuan Zheng, Shu-Juan Zhang, Guo-Ping Sheng
Index: Chemosphere 54(7) , 789-94, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The reductive degradation of nitrobenzene (NB) by zero-valent iron was investigated. Experimental results showed that the degradation of NB was influenced by pH and NB concentration. The optimum pH value was found to be 3.0 for the reductive degradation of NB in the tested pH ranges of 3.0-12.0. The formation rate of aniline, a major reductive product of NB, followed zero-order kinetics at various pH levels. Furthermore, GC/MS analysis showed that aniline, azobenzene and azoxybenzene were the reductive products of NB by zero-valent iron. With the analysis of the products with GC/MS and FTIR, possible reductive pathways of NB by zero-valent iron were suggested.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
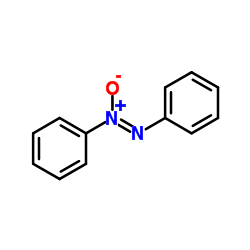 |
fentoxan
CAS:495-48-7 |
C12H10N2O |
|
Reduction of nitroarenes to azoxybenzenes by potassium boroh...
2011-01-01 [Molecules 16 , 3563-3568, (2011)] |
|
[A case of suicide suspected of poisoning from taking some a...
1991-04-01 [Nihon Hoigaku. Zasshi 45(2) , 158-65, (1991)] |
|
[Distribution and metabolism of azoxybenzene in the rat].
1989-05-01 [Z. Gesamte Hyg. 35(5) , 255-7, (1989)] |
|
Investigations of myelotoxic effects in rats.
1991-01-01 [Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 14 , 83-7, (1991)] |
|
Chloracne and chloracnegens.
1985-10-01 [J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 13(4) , 539-58, (1985)] |