Sequence-dependent reactivity of model peptides with glyceraldehyde.
N Mori, Y Bai, H Ueno, J M Manning
Index: Carbohydr. Res. 189 , 49-63, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Glyceraldehyde reacted faster with tripeptides than with dipeptides. The pH profiles of the reactions with tripeptides displayed optima in the range of 8.5-10.0, approximately 1-2 pH units higher than found with dipeptides. The second amino acid residue influences not only the rate of reaction but also the extent of formation of the product of the Amadori rearrangement, the ketoamine. The presence of histidine as the second amino acid residue of either di- or tri-peptides greatly accelerated the rate of reaction perhaps by facilitating the rearrangement. Conventional amino acid analysis and liquid chromatography procedures have been used to detect intermediates and the ketoamine product. 1H-N.m.r. analysis of the reduced adducts was consistent with the assigned structures.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
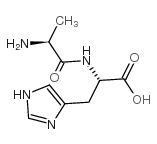 |
H-Ala-His-OH
CAS:3253-17-6 |
C9H14N4O3 |
|
Carbonic anhydrase activators: high affinity isozymes I, II,...
2002-01-17 [J. Med. Chem. 45(2) , 284-91, (2002)] |
|
A potentiometric and 51V NMR study of the aqueous H+/H2VO4-/...
2001-01-05 [Chemistry 7(1) , 251-7, (2001)] |
|
Investigation on the formation and the determination of gamm...
2000-12-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(12) , 6317-24, (2000)] |
|
Coordination features of difunctionalized beta-cyclodextrins...
2004-02-01 [J. Inorg. Biochem. 98(2) , 254-65, (2004)] |
|
Effect of carnosine and related compounds on the inactivatio...
2002-01-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66 , 36-43, (2002)] |