| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
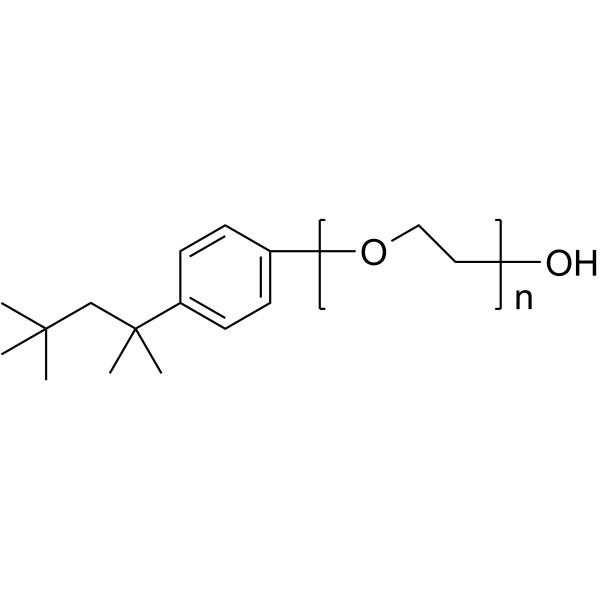 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
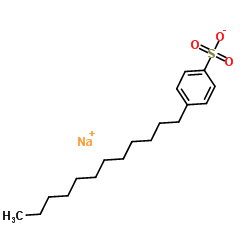 |
sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate
CAS:25155-30-0 |
|
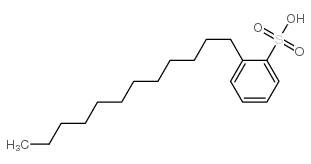 |
Dodecylbenzenesulphonic acid
CAS:27176-87-0 |