A novel biotinylated suicide inhibitor for directed molecular evolution of lipolytic enzymes.
H J Deussen, S Danielsen, J Breinholt, T V Borchert
Index: Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8(3) , 507-13, (2000)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A bifunctional activity label (8) for directed molecular evolution of lipolytic enzymes has been designed and synthesized. The structure is composed of a 4-nitrophenyl activated phosphonate, that is, a suicide substrate of lipases/esterases, connected to a biotin moiety through a spacer containing a disulfide bridge. The phosphonate (3) was prepared by Michaelis-Arbuzov reaction of trimethylsilyl-protected 11-bromoundecanol (2) with triethyl phosphite. The deprotected omega-hydroxyalkylphosphonate (4) was transformed into an active N-hydroxysuccinimide carbonate (5) followed by 4-nitrophenyl activation of the phosphonate using standard procedures. The biotinylated phosphonate inhibitor (8) was then synthesised by coupling the phosphonate inhibitor (6) to the epsilon-amino-caproic acid and cystamine containing biotinyl spacer (7). The function of all relevant groups of the final activity label (8) (biotin-label, cleavable disulfide bridge, phosphonate-inhibitor) have been successfully tested with the commercial lipase Lipolase (Novo Nordisk). Hence, a tool for directed molecular evolution of lipolytic enzymes has been developed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
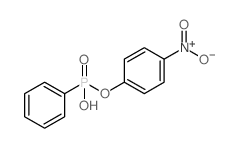 |
4-Nitrophenyl hydrogen phenylphosphonate
CAS:57072-35-2 |
C12H10NO5P |
|
Detection of catalytic monoclonal antibodies.
1992-04-01 [Anal. Biochem. 202(1) , 35-9, (1992)] |
|
The catalytic mechanism of bovine intestinal 5'-nucleotide p...
1983-06-10 [J. Biol. Chem. 258(11) , 6941-6, (1983)] |
|
Positron emission tomography scan in cortical visual loss in...
1999-07-01 [Ophthalmology 106(7) , 1287-91, (1999)] |
|
Hydrolysis of a phosphonate ester catalyzed by an enzyme fro...
1979-10-01 [Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 197(1) , 364-6, (1979)] |
|
[Study of the enzymatic hydrolysis of a phosphonic ester usi...
1979-01-01 [Biochimie 61(9) , 1091-4, (1979)] |