Theory of electric characteristics of the lipid/PVC/DOPP membrane and PVC/DOPP membrane in response to taste stimuli.
K Oohira, K Toko, Koji Oohira, Kiyoshi Toko
Index: Biophys. Chem. 61(1) , 29-35, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Electric characteristics of two kinds of membranes in response to NaCl and quinine were theoretically studied; one membrane composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and dioctylphenylphosphonate (DOPP), and the other a lipid/PVC/DOPP membrane containing PVC, DOPP and a negatively charged lipid. We develop a theory by taking into account both the surface electric potential and the diffusion potential within the membrane and succeed in interpreting the observed data. On increasing the NaCl concentration, the lipid/PVC/DOPP membrane changes from weakly charged state to fully charged state by dissociation of H+ from the lipids. The hydrophobic interaction between quinine and the PVC/DOPP membrane was strong enough to overcome the electric repulsion.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
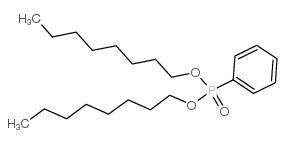 |
Phosphonic acid,P-phenyl-, dioctyl ester
CAS:1754-47-8 |
C22H39O3P |
|
A novel approach for honey pollen profile assessment using a...
2015-11-05 [Anal. Chim. Acta 900 , 36-45, (2015)] |
|
Ionophore-based potentiometric sensors for the flow-injectio...
2011-01-01 [Sensors (Basel.) 11(1) , 1028-42, (2011)] |
|
Amodiaquine polymeric membrane electrode.
2006-04-11 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 41(1) , 70-6, (2006)] |
|
PVC membrane based potentiometric sensors for uranium determ...
2001-07-06 [Talanta 54(6) , 1153-61, (2001)] |
|
Study of sweet taste evaluation using taste sensor with lipi...
2004-07-15 [Biosens. Bioelectron. 19(12) , 1559-63, (2004)] |