Stereo- and regioselective hydroxylation of alpha-ionone by Streptomyces strains.
S Lutz-Wahl, P Fischer, C Schmidt-Dannert, W Wohlleben, B Hauer, R D Schmid
Index: Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64(10) , 3878-81, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A total of 215 Streptomyces strains were screened for their capacity to regio- and stereoselectively hydroxylate beta- and/or alpha-ionone to the respective 3-hydroxy derivatives. With beta-ionone as the substrate, 15 strains showed little conversion to 4-hydroxy- and none showed conversion to the 3-hydroxy product as desired. Among these 15 Streptomyces strains, S. fradiae Tü 27, S. arenae Tü 495, S. griseus ATCC 13273, S. violaceoniger Tü 38, and S. antibioticus Tü 4 and Tü 46 converted alpha-ionone to 3-hydroxy-alpha-ionone with significantly higher hydroxylation activity compared to that of beta-ionone. Hydroxylation of racemic alpha-ionone [(6R)-(-)/(6S)-(+)] resulted in the exclusive formation of only the two enantiomers (3R,6R)- and (3S, 6S)-hydroxy-alpha-ionone. Thus, the enzymatic hydroxylation of alpha-ionone by the Streptomyces strains tested proceeds with both high regio- and stereoselectivity.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
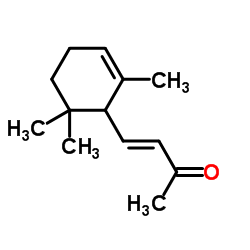 |
alpha-Ionone
CAS:127-41-3 |
C13H20O |
|
Biosynthesis of α- and β-ionone, prominent scent compounds, ...
2012-01-01 [Acta Biochim. Pol. 59(1) , 79-81, (2012)] |
|
CYP264B1 from Sorangium cellulosum So ce56: a fascinating no...
2012-07-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 95(1) , 123-33, (2012)] |
|
New attractants for males of the solanaceous fruit fly Bactr...
2008-12-01 [J. Chem. Ecol. 34(12) , 1532-5, (2008)] |
|
Enhancement of attraction of alpha-ionol to male Bactrocera ...
2001-02-01 [J. Econ. Entomol. 94(1) , 39-46, (2001)] |
|
Efficient terpene hydroxylation catalysts based upon P450 en...
2005-08-21 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 3(16) , 2930-4, (2005)] |