The effect of acidosis on adenosine release from cultured rat forebrain neurons.
Christina R Zamzow, Ratna Bose, Fiona E Parkinson
Index: Brain Res. 1082(1) , 23-31, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
During cerebral ischemia, dysregulated glutamate release activates N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors which promotes excitotoxicity and intracellular acidosis. Ischemia also induces cellular adenosine (ADO) release, which activates ADO receptors and reduces neuronal injury. The aim of this research was to determine if decreasing intracellular pH (pH(i)) enhances ADO release from neurons. Rat forebrain neurons were incubated with NMDA, acetate, propionate, 5-(N)-ethyl-N-isopropyl amiloride (EIPA) or low pH buffer. pH(i) was determined with the fluorescent dye 2',7'-bis(2-carboxyethyl)-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein acetoxymethyl ester (BCECF-AM) and cellular release of ADO was assayed. NMDA decreased pH(i) and increased ADO release from neurons. Acetate and propionate decreased pH(i) and evoked ADO release from neurons. EIPA, an inhibitor of sodium hydrogen exchanger 1 (NHE1), enhanced the acidosis in neurons but did not enhance ADO release. Decreasing extracellular pH (pH(e)) to 6.8 or 6.45 significantly decreased pH(i) in neurons, but was not consistently associated with increased ADO release. The main finding of this study was that acidosis per se did not enhance ADO release from neurons.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
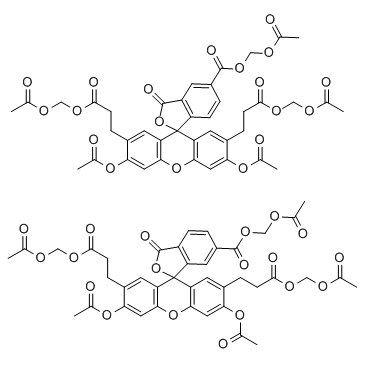 |
BCECF-AM
CAS:117464-70-7 |
C40H36O19 |
|
Fast loading ester fluorescent Ca2+ and pH indicators into p...
2012-01-01 [J. Plant Res. 125(1) , 185-95, (2012)] |
|
Role of the plasma membrane calcium adenosine triphosphatase...
2006-08-01 [J. Neurosci. Res. 84(2) , 326-37, (2006)] |
|
Platelet-activating factor stimulates cytoplasmic alkaliniza...
2004-11-15 [J. Cell Sci. 117(Pt 24) , 5749-57, (2004)] |
|
Freeze-dried rehydrated human blood platelets regulate intra...
2006-06-01 [Transfusion 46(6) , 1029-37, (2006)] |
|
Activity and expression of Na+/H+ exchanger isoforms in the ...
2005-05-01 [Pflugers Arch. 450(2) , 123-30, (2005)] |