| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
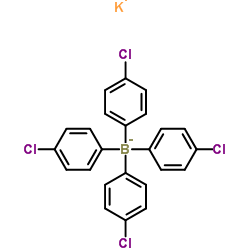 |
Potassium tetrakis(4-chlorophenyl)borate(1-)
CAS:14680-77-4 |
|
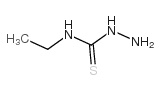 |
Hydrazinecarbothioamide,N-ethyl-
CAS:13431-34-0 |