Effects of the antithrombotic drug suloctidil on low density lipoprotein processing and cholesterol metabolism in cultured human fibroblasts.
C Mazière, J C Mazière, N E Houtia, J Lauga, J Polonovski
Index: J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 26(1) , 3-6, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Human foetal lung fibroblasts were pretreated for 24 h with the antithrombotic drug, suloctidil (1 to 10 mumol/l), which induced a dose-dependent increase in LDL binding, uptake and degradation. At 10 mumol/l suloctidil, the respective increases in these parameters were 40%, 80% and 50%. The same treatment also resulted in increases of 1.5 to 2-fold in the synthesis of sterols, fatty acids and triacylglycerols from sodium acetate. In contrast, the esterification of cholesterol with oleic acid was specifically decreased by 35% by 24 h pretreatment of fibroblasts with 10 mumol/l suloctidil. A similar decrease of cholesterol esterification was observed in cholesterol-laden fibroblasts. It is suggested that these effects of suloctidil on LDL processing and cholesterol metabolism are related to the amphiphilic characteristics of the drug and to its calcium-blocking properties.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
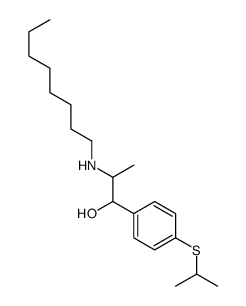 |
Suloctidil
CAS:54767-75-8 |
C20H35NOS |
|
A repurposing approach identifies off-patent drugs with fung...
2013-02-01 [Eukaryotic Cell 12(2) , 278-87, (2013)] |
|
Inhibition of platelet thromboxane generation by suloctidil ...
1986-01-01 [Haemostasis 16(5) , 362-8, (1986)] |
|
Suloctidil-induced hepatotoxicity.
[Gastroenterology 95(2) , 490-1, (1988)] |
|
Suloctidil hepatitis: a case presentation.
1987-10-01 [Ir. J. Med. Sci. 156(10) , 290-1, (1987)] |
|
Effect of suloctidil on tomographically quantitated platelet...
1986-07-01 [Am. J. Cardiol. 58(1) , 152-6, (1986)] |