Effects of triflumuron on the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranichydae).
F J Saenz de Cabezón, I Pérez-Moreno, V Marco
Index: Exp. Appl. Acarol. 26(1-2) , 71-8, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effects of triflumuron on the mortality, fecundity, and fertility of the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae, were evaluated in the laboratory. No differences in toxicity for larvae, protonymphs and deutonymphs were observed, but immature stages were 3.8-times more susceptible than adults at the LC50. The compound exhibited a direct contact ovicidal activity influenced by eggs age. 48-72 h old eggs were significantly more sensitive than eggs of the other age classes. No hatch inhibition was observed in eggs laid by treated adult females using a sublethal dose at two physiological times (<12 and 48-72 h old). However. fecundity decreased in younger treated females, but it increased in the older-ones. The toxicity for immatures and eggs, and the sublethal effects described suggest that triflumuron could be an interesting incorporation in integrated pest programs of T. urticae.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
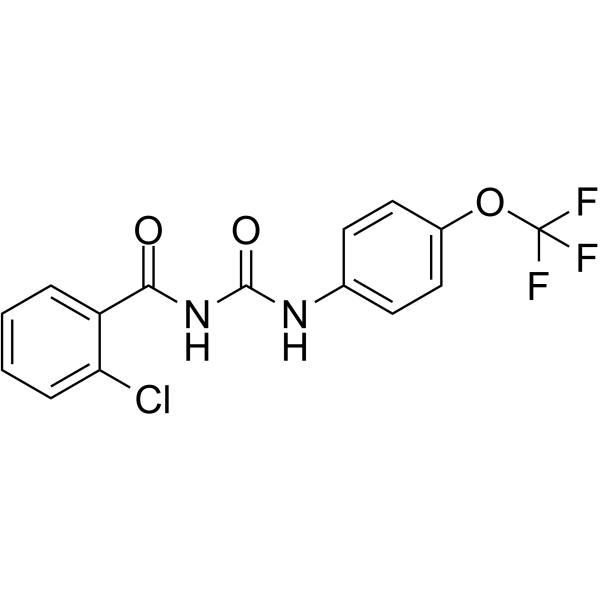 |
Triflumuron
CAS:64628-44-0 |
C15H10ClF3N2O3 |
|
Comparison of two ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid micr...
2014-08-22 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1356 , 1-9, (2014)] |
|
Multi-residue method for determination of 238 pesticides in ...
2014-11-26 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(47) , 11449-56, (2014)] |
|
Resistance status of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotars...
2007-01-01 [J. Insect Sci. 7 , 1-7, (2007)] |
|
Benzoylphenylurea residues in peppers and zucchinis grown in...
2004-02-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 60(2) , 183-90, (2004)] |
|
Multiresidue determination of pesticides in plants by high-p...
1998-10-09 [J. Chromatogr. A. 823(1-2) , 11-6, (1998)] |