Treatment of diazo dye C.I. Reactive Black 5 in aqueous solution by combined process of interior microelectrolysis and ozonation.
Xiaoyan Guo, Yaping Cai, Zhongbo Wei, Haifeng Hou, Xi Yang, Zunyao Wang
Index: Water Sci. Technol. 67(8) , 1880-5, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Interior microelectrolysis (IM) as a pretreatment process was effective to treat Reactive Black 5 (RB5) in this study. The removal rates of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total organic carbon (TOC) and color were 46.05, 39.99 and 98.77%, respectively, when this process was conducted under the following optimal conditions: the volumetric ratio between iron scraps and active carbon (AC) (V(Fe)/V(C)) 1.0, pH 2.0, aeration dosage 0.6 L/min, and reaction time 100 min. Contaminants could be further removed by ozonation. After subsequent ozonation for 200 min, the solution could be completely decolorized, and the COD and TOC removal rates were up to 77.78 and 66.51%, respectively. In addition, acute toxicity tests with Daphnia magna showed that pretreatment by IM generated effluents that were more toxic when compared with the initial wastewater, and the toxicity was reduced after subsequent ozonation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
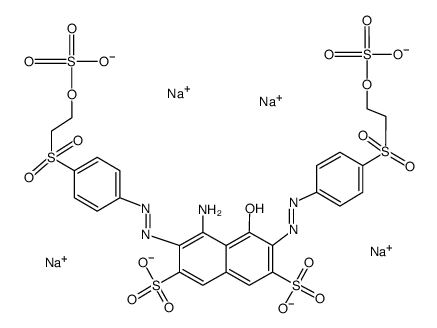 |
reactive black 5
CAS:17095-24-8 |
C26H21N5Na4O19S6 |
|
Comparative analysis of bioremediation potential of adapted ...
2011-06-01 [Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 14(11) , 610-8, (2011)] |
|
Using iron-loaded sepiolite obtained by adsorption as a cata...
2013-09-01 [Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 20(9) , 5983-93, (2013)] |
|
Application of response surface methodology to optimize deco...
2012-10-15 [J. Environ. Manage. 108 , 84-91, (2012)] |
|
Photo-Fenton oxidation of azo dye Reactive Black B using an ...
2013-04-01 [Water Environ. Res. 85(4) , 340-5, (2013)] |
|
Sprayed nanostructured TiO2 films for efficient photocatalyt...
2012-12-05 [J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 117 , 19-26, (2012)] |