Antioxidant activities of isoflavones from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury in rats.
Sang Hoon Jung, Yeon Sil Lee, Soon Sung Lim, Sanghyun Lee, Kuk Hyun Shin, Yeong Shik Kim
Index: Arch. Pharm. Res. 27(2) , 184-8, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The present study was carried out to clarify whether tectorigenin and tectoridin isolated from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis (Iridaceae) inhibit hepatic damage induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-intoxication in rats by the experimental methods in vitro and in vivo. Tectorigenin and tectoridin exhibited a significant decrease in serum transaminase activities elevated by hepatic damage induced by CCl4-intoxication in rats, as well as in a lipid peroxidation causing a significant decrease in malondialdehyde (MDA) production by thiobarbituric acid (TBA)-reactant assay. Both compounds also showed strong increase in the antioxidant enzymes such as hepatic cytosolic superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px) activities in CCl4-intoxicated rats. These results suggested that tectorigenin and tectoridin isolated from the rhizomes of B. chinensis possess not only the antioxidative, but also the hepatoprotective activities in CCl4-intoxicated rats.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
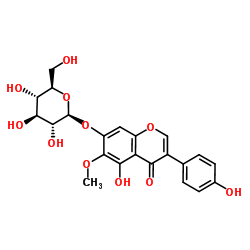 |
tectoridin
CAS:611-40-5 |
C22H22O11 |
|
Tectorigenin inhibits IFN-gamma/LPS-induced inflammatory res...
2008-11-01 [Arch. Pharm. Res. 31(11) , 1447-56, (2008)] |
|
Tectoridin, a poor ligand of estrogen receptor alpha, exerts...
2009-03-31 [Mol. Cells 27(3) , 351-7, (2009)] |
|
Microbial transformation and bioactivation of isoflavones fr...
2009-07-01 [J. Nat. Med. 63(3) , 254-60, (2009)] |
|
Inhibitory activity of isoflavones of Pueraria flowers on ni...
2009-06-01 [J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 11(6) , 471-81, (2009)] |
|
Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis-inhibitory action of tectorige...
2004-07-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27(7) , 1099-102, (2004)] |