| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
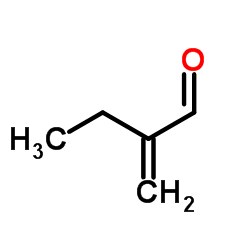 |
2-Ethacrolein
CAS:922-63-4 |
|
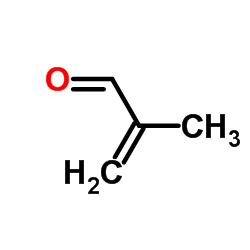 |
Methylpropenal
CAS:78-85-3 |