Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
1986-11-26
Xanthine oxidase-catalyzed DNA binding of dihydrodiol derivatives of nitro-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
K K Colvert, P P Fu
Index: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 141(1) , 245-50, (1986)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Xanthine oxidase, a mammalian nitroreductase, catalyzed the covalent binding of a series of nitro-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (nitro-PAHs) trans-dihydrodiols to DNA. Some of the trans-dihydrodiols bound to DNA to a greater extent than their parent nitro-PAHs; however, when the dihydrodiol moiety was peri to the nitro substituent low levels of binding were observed. These data illustrate that ring-oxidation and hydrolysis of nitro-PAHs to their trans-dihydrodiols followed by nitroreduction is a potential metabolic pathway leading to DNA adducts in mammals.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
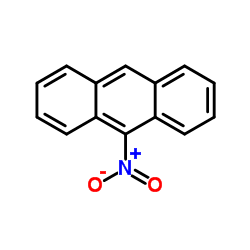 |
9-Nitroanthracene
CAS:602-60-8 |
C14H9NO2 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Preparation, Structural Determination, and Characterization ...
2015-11-09 [Chemistry 21 , 16411-20, (2015)] |
|
9-Nitroanthracene derivative as a precursor of anthraquinone...
2007-06-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15(11) , 3869-73, (2007)] |
|
HPLC retention behavior of poly-aromatic-hydrocarbons on ami...
2004-01-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 52(1) , 41-6, (2004)] |
|
Contamination is a frequent confounding factor in toxicology...
2004-01-01 [Int. J. Toxicol. 23(5) , 335-44, (2004)] |
|
Application of 9-nitroanthracene as a matrix for laser desor...
2004-01-01 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 18(3) , 360-2, (2004)] |