The effect of fungal ribosome inactivating proteins upon feeding choice in C. freemani, and indications of a mutualistic relationship with A. restrictus. Environmental mycology.
T Brandhorst, P F Dowd, W R Kenealy
Index: Mycopathologia 152(3) , 155-8, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Carpophilus freemani beetles' feeding on the fungus Aspergillus nidulans was substantially inhibited when A. nidulans was transformed and induced to secrete the ribosome inactivating protein, restrictocin (genetic source: Aspergillus restrictus). No inhibition of feeding was observed when A. nidulans was transformed and induced to produce an inactive form of restrictocin with a single amino-acid substitution in the active site. Similarly, there was no inhibition of feeding upon transgenic strains when the production of restrictocin was not induced. Feeding inhibition of C. freemani by restrictocin requires that the ribonuclease be active and is not due to other characteristics of the protein or the transgenic host fungus.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
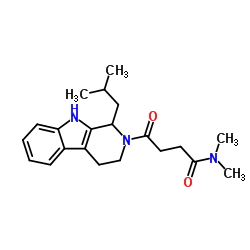 |
Restrictocin
CAS:1406-72-0 |
C21H29N3O2 |
|
The ribotoxin restrictocin recognizes its RNA substrate by s...
2011-04-12 [Biochemistry 50(14) , 3004-13, (2011)] |
|
Role of individual cysteine residues and disulfide bonds in ...
1999-08-03 [Biochemistry 38(31) , 10052-8, (1999)] |
|
Mechanism of specific target recognition and RNA hydrolysis ...
2001-08-07 [Biochemistry 40(31) , 9115-24, (2001)] |
|
Electrostatic interactions guide the active site face of a s...
2008-08-26 [Biochemistry 47(34) , 8912-8, (2008)] |
|
[Antibody detection in patients with invasive aspergillosis]...
2004-01-01 [Mycoses 47 Suppl 1 , 55-9, (2004)] |