| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
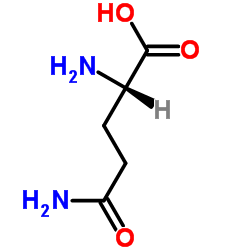 |
L-Alanyl-L-Glutamine
CAS:39537-23-0 |
|
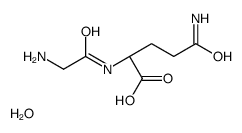 |
Glycyl-L-glutamine Monohydrate
CAS:172669-64-6 |