(99m)Tc complexes with activated ester functions; ligands comprising a 3,4-diamino-benzoate backbone.
Osmar Calderon Sanchez, Ashour Mohammed, Claudia Bauer, Markus Wolf, Björn Wängler, Walter Mier, Uwe Haberkorn, Raoul Mocelo, Michael Eisenhut
Index: Nucl. Med. Biol. 33(3) , 381-90, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Preformed (99m)Tc chelates with an activated ester function are useful for the gentle labeling of proteins (precomplexation route). In this context, new heterobifunctional ligands derived from 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorophenyl (TFP) 3,4-diamino-benzoates (OC1, OC3, OC4) were synthesized. Their corresponding (99m)Tc-complexation and protein-conjugation characteristics were elucidated and compared with the results previously reported using 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorophenyl N-(S-benzoylthioacetyl)glycylglycyl-p-aminobenzoate (OC2). The reaction temperatures and the reaction time markedly influenced complexation yields. Compared with OC2, the (99m)Tc-chelate formation with OC1 and OC4 was more effective, showing radiochemical yields of 60% and 70% within 20 min, respectively. Owing to steric hindrance, the complexation of OC3, however, did not exceed 10%. No-carrier-added (99m)Tc complexes were conjugated at pH 10 with the anti-EGF-receptor monoclonal antibody MAb425, resulting in labeling yields of 14% for (99m)Tc-OC1 and 7% for (99m)Tc-OC4 after incubating for 20 min at 30 degrees C. Increasing the temperature to 40 degrees C improved these results by 14% and 3%, respectively. As compared with (99m)Tc-OC2, which provides the chelating substituent at the 4-phenyl position only, the application of 3,4-phenyl substituents proved less appropriate for protein conjugation. However, the 3,4-diaminobenzoate backbone may be attractive for an alternative design of novel (99m)Tc N2S2 or N3S complexes, because they show excellent complexation characteristics.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
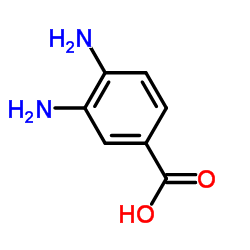 |
3,4-Diaminobenzoicacid
CAS:619-05-6 |
C7H8N2O2 |
|
Synthesis of lucifensin by native chemical ligation and char...
2014-09-01 [J. Pept. Sci. 20(9) , 725-35, (2014)] |
|
Reducing the alkali cation adductions of oligonucleotides us...
2003-08-15 [Anal. Chem. 75(16) , 4223-8, (2003)] |
|
Clinical laboratory differentiation of Legionellaceae family...
1984-05-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 19(5) , 583-7, (1984)] |
|
Synthesis and biological activity of certain alkyl 5-(alkoxy...
1992-02-07 [J. Med. Chem. 35 , 539, (1992)] |
|
A reversible protection strategy to improve Fmoc-SPPS of pep...
2011-11-04 [ChemBioChem. 12(16) , 2488-94, (2011)] |