| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
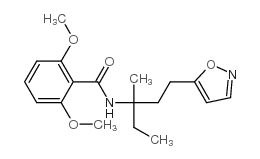 |
isoxaben
CAS:82558-50-7 |
|
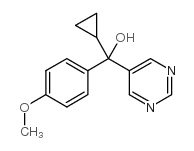 |
Ancymidol
CAS:12771-68-5 |