| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
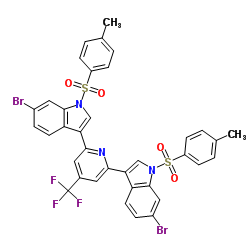 |
Thioredoxin reductase
CAS:9074-14-0 |
|
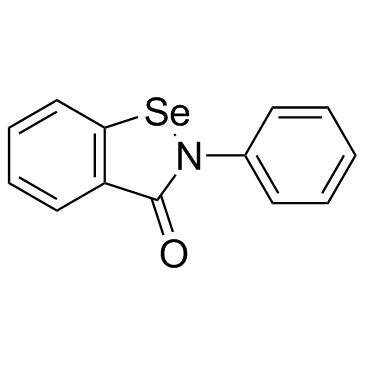 |
Ebselen
CAS:60940-34-3 |