| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
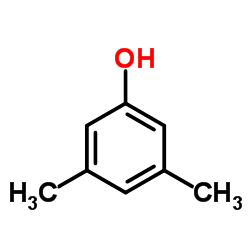 |
3,5-Dimethylphenol
CAS:108-68-9 |
|
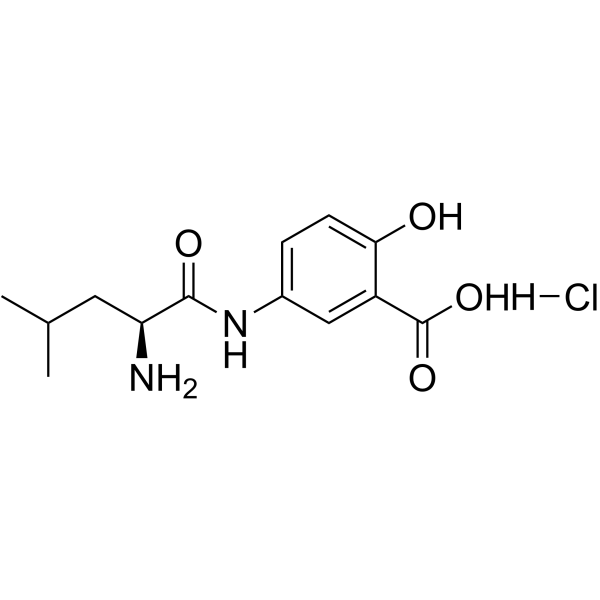 |
L-LEUCINE 3-CARBOXY-4-HYDROXYANILIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
CAS:73801-31-7 |