NO-1886 suppresses diet-induced insulin resistance and cholesterol accumulation through STAT5-dependent upregulation of IGF1 and CYP7A1.
Qinkai Li, Weidong Yin, Manbo Cai, Yi Liu, Hongjie Hou, Qingyun Shen, Chi Zhang, Junxia Xiao, Xiaobo Hu, Qishisan Wu, Makoto Funaki, Yutaka Nakaya
Index: J. Endocrinol. 1st ed., 204 , 47-56, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Insulin resistance and dyslipidemia are both considered to be risk factors for metabolic syndrome. Low levels of IGF1 are associated with insulin resistance. Elevation of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) concomitant with depression of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) increase the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Liver secretes IGF1 and catabolizes cholesterol regulated by the rate-limiting enzyme of bile acid synthesis from cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1). NO-1886, a chemically synthesized lipoprotein lipase activator, suppresses diet-induced insulin resistance with the improvement of HDL-C. The goal of the present study is to evaluate whether NO-1886 upregulates IGF1 and CYP7A1 to benefit glucose and cholesterol metabolism. By using human hepatoma cell lines (HepG2 cells) as an in vitro model, we found that NO-1886 promoted IGF1 secretion and CYP7A1 expression through the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5). Pretreatment of cells with AG 490, the inhibitor of STAT pathway, completely abolished NO-1886-induced IGF1 secretion and CYP7A1 expression. Studies performed in Chinese Bama minipigs pointed out an augmentation of plasma IGF1 elicited by a single dose administration of NO-1886. Long-term supplementation with NO-1886 recovered hyperinsulinemia and low plasma levels of IGF1 suppressed LDL-C and facilitated reverse cholesterol transport by decreasing hepatic cholesterol accumulation through increasing CYP7A1 expression in high-fat/high-sucrose/high-cholesterol diet minipigs. These findings indicate that NO-1886 upregulates IGF1 secretion and CYP7A1 expression to improve insulin resistance and hepatic cholesterol accumulation, which may represent an alternative therapeutic avenue of NO-1886 for T2DM and metabolic syndrome.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
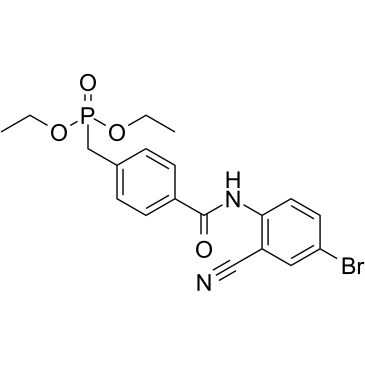 |
Ibrolipim
CAS:133208-93-2 |
C19H20BrN2O4P |
|
Effects of NO-1886 on inflammation-associated cytokines in h...
2006-07-01 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 540(1-3) , 139-46, (2006)] |
|
Evaluation of induction potency of new drug candidates on CY...
2009-01-01 [Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 24(5) , 446-50, (2009)] |
|
NO-1886 (ibrolipim), a lipoprotein lipase-promoting agent, a...
2006-02-01 [Metab. Clin. Exp. 55(2) , 151-8, (2006)] |
|
NO-1886, a lipoprotein lipase activator, attenuates vascular...
2007-01-12 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 554(2-3) , 183-90, (2007)] |
|
NO-1886 ameliorates glycogen metabolism in insulin-resistant...
2012-02-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 64(2) , 293-301, (2012)] |