| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
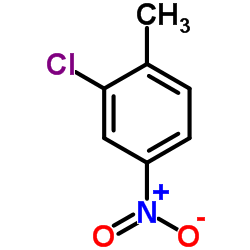 |
CNT
CAS:121-86-8 |
|
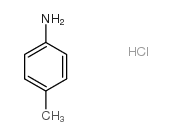 |
4-Methylaniline hydrochloride
CAS:540-23-8 |
|
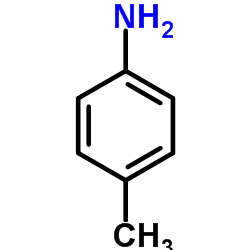 |
p-Toluidine
CAS:106-49-0 |