Transformation of the herbicide 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile to the persistent metabolite 2,6-dichlorobenzamide (BAM) by soil bacteria known to harbour nitrile hydratase or nitrilase.
Maria Sommer Holtze, Jan Sørensen, Hans Christian B Hansen, Jens Aamand
Index: Biodegradation 17(6) , 503-10, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In soil the herbicide 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile (dichlobenil) is degraded to the persistent metabolite 2,6-dichlorobenzamide (BAM) which has been detected in 19% of samples taken from Danish groundwater. We tested if common soil bacteria harbouring nitrile-degrading enzymes, nitrile hydratases or nitrilases, were able to degrade dichlobenil in vitro. We showed that several strains degraded dichlobenil stoichiometrically to BAM in 1.5-6.0 days; formation of the amide intermediate thus showed nitrile hydratase rather than nitrilase activity, which would result in formation of 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid. The non-halogenated analogue benzonitrile was also degraded, but here the benzamide intermediate accumulated only transiently showing nitrile hydratase followed by amidase activity. We conclude that a potential for dichlobenil degradation to BAM is found commonly in soil bacteria, whereas further degradation of the BAM intermediate could not be demonstrated.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
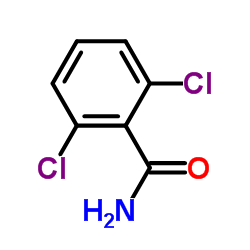 |
BAM
CAS:2008-58-4 |
C7H5Cl2NO |
|
Study of degradation intermediates formed during electrochem...
2014-08-01 [Chemosphere 109 , 84-91, (2014)] |
|
Microbial degradation of the benzonitrile herbicides dichlob...
2008-07-01 [Environ. Pollut. 154(2) , 155-68, (2008)] |
|
2,6-Dichlorobenzamide (BAM) herbicide mineralisation by Amin...
2010-12-01 [Environ. Pollut. 158(12) , 3618-25, (2010)] |
|
Inherent mineralization of 2,6-dichlorobenzamide (BAM) in un...
2011-10-01 [Environ. Pollut. 159(10) , 2801-7, (2011)] |
|
C and N isotope fractionation during biodegradation of the p...
2012-02-07 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(3) , 1447-54, (2012)] |