| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
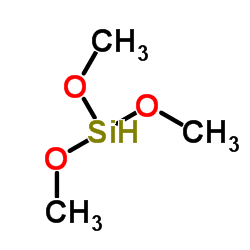 |
Trimethoxysilane
CAS:2487-90-3 |
|
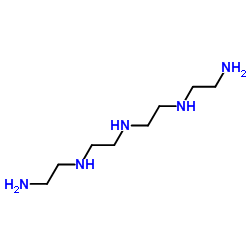 |
tetraethylenepentamine
CAS:112-57-2 |
|
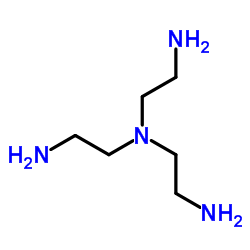 |
Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine
CAS:4097-89-6 |