| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
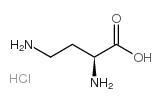 |
H-Dab.HCl
CAS:1482-98-0 |
|
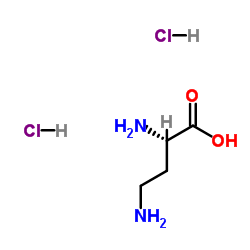 |
L-2,4-Diaminobutyric acid dihydrochloride
CAS:1883-09-6 |