Preliminary study of responses in mussel (Mytilus edilus) exposed to bisphenol A, diallyl phthalate and tetrabromodiphenyl ether.
N Aarab, S Lemaire-Gony, E Unruh, P D Hansen, B K Larsen, O K Andersen, J F Narbonne
Index: Aquat. Toxicol. 78 Suppl 1 , S86-92, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Environmental pollutants with hormonal activity including bisphenol, diallyl phtalate and tetrabromodiphenyl ether, have the potential to alter gonadal development and reproduction in aquatic wildlife. Little is known about the biological impact of environmentally relevant concentrations in mussels. To investigate some aspects of their potential estrogenic action, mussels were continuously exposed during 3 weeks. Gonadal development and vitellogenin like protein levels were examined. Bisphenol (50 microg/l) induced the expression of phospho-proteins in females and spawning in both sexes. Diallyl phthalate and tetrabromodiphenyl ether decreased phospho-protein levels in both sexes and induced spawning in males. Moreover, severe damaging effects on ovarian follicles and ovocytes were observed in both bisphenol A- and tetrabromodiphenyl ether-exposed female mussels.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
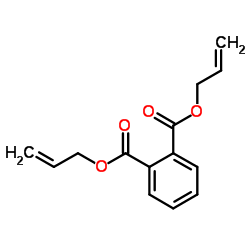 |
Diallyl phthalate
CAS:131-17-9 |
C14H14O4 |
|
Determination of free and total phthalates in commercial who...
2015-12-01 [J. Dairy Sci. 98 , 8278-84, (2015)] |
|
Development of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction comb...
2007-11-23 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1172(2) , 105-12, (2007)] |
|
[Determination of 23 phthalate esters in food by solid-phase...
2012-01-01 [Se Pu 30(1) , 27-32, (2012)] |
|
A proteomics based approach to assessing the toxicity of bis...
2010-04-01 [Chemosphere 79(5) , 595-604, (2010)] |
|
Effect of ultrasonic separation on the structure and propert...
2008-04-01 [Ultrason. Sonochem. 15(4) , 364-9, (2008)] |