Induction of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in mussels exposed to bisphenol A, diallyl phthalate and tetrabromodiphenyl ether-47.
Janina Barsiene, Janina Syvokiene, Anne Bjornstad
Index: Aquat. Toxicol. 78 Suppl 1 , S105-8, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Analysis of micronuclei, nuclear buds, bi-polynucleated and fragmented-apoptotic cells was performed in gills of blue mussels exposed for 3 weeks to sublethal concentrations of bisphenol A, diallyl phthalate (for the both nominal concentration 50 ppb) and to tetrabromodiphenyl ether-47 (nominal concentration 5 ppb). Fourteen specimens from each treatment and control group were used for the analysis. Our results demonstrated a significant increase in micronuclei frequency after the treatment with bisphenol A (P=0.0243), diallyl phthalate (P=0.0005) and tetrabromodiphenyl ether-47 (P<0.0001; Mann-Whitney U-test). Induction of bi-nucleated (P=0.0028), fragmented-apoptotic (P=0.0004) cells and nuclear buds (P=0.0101) was found in mussels exposed to tetrabromodiphenyl ether-47 while treatment with diallyl phthalate increased the level of fragmented-apoptotic cells (P=0.0283). Bisphenol A was the only agent that resulted only in induction of micronuclei but not any other kind of nuclear injuries.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
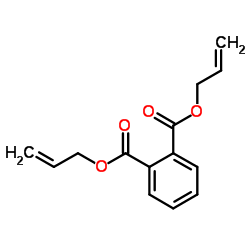 |
Diallyl phthalate
CAS:131-17-9 |
C14H14O4 |
|
Determination of free and total phthalates in commercial who...
2015-12-01 [J. Dairy Sci. 98 , 8278-84, (2015)] |
|
Development of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction comb...
2007-11-23 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1172(2) , 105-12, (2007)] |
|
[Determination of 23 phthalate esters in food by solid-phase...
2012-01-01 [Se Pu 30(1) , 27-32, (2012)] |
|
A proteomics based approach to assessing the toxicity of bis...
2010-04-01 [Chemosphere 79(5) , 595-604, (2010)] |
|
Effect of ultrasonic separation on the structure and propert...
2008-04-01 [Ultrason. Sonochem. 15(4) , 364-9, (2008)] |