| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
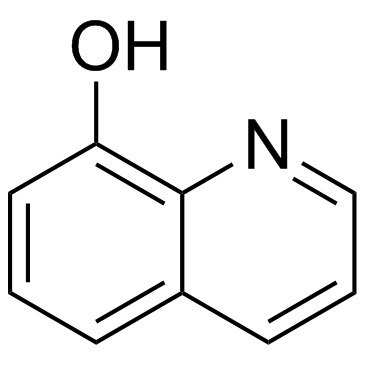 |
8-Hydroxyquinoline
CAS:148-24-3 |
|
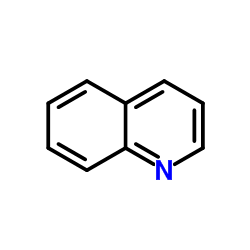 |
leucoline
CAS:91-22-5 |
|
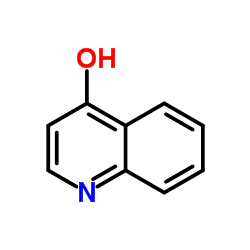 |
4-quinolone
CAS:611-36-9 |