A quantitative analysis to unveil specific binding proteins for bioactive compounds.
Tomonori Arai, Masayoshi Uehata, Hiroyuki Akatsuka, Tsutomu Kamiyama
Index: Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 26(4) , 249-54, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The mechanisms of the action of bioactive compounds discovered via 'black box' assays using phenotypic indicators generally remain unknown, with the major challenges being the identification of target proteins. In this study, we aimed to develop an efficient methodology to unveil target proteins that are rarely characterised. Proof-of-concept experiments were performed using N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide (W-7), a well-known calmodulin (CaM) antagonist, as a bait compound. The results showed that in our methodology CaM was identified as a W-7-specific binding protein in the cytosolic fraction of a rat brain extract, whereas other proteins acquired in the same experiment were recognised as non-specific binding proteins. The binding affinity of CaM to W-7 is not very high (dissociation constant: 1.6 × 10(-5) M), showing that the recognition specificity is applicable to compounds with very low binding affinities.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
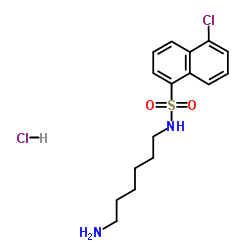 |
W-7 hydrochloride
CAS:61714-27-0 |
C16H22Cl2N2O2S |
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical p...
2009-10-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009)] |
|
Calmodulin antagonists induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosi...
2014-01-01 [BMC Cancer 14 , 882, (2014)] |
|
Calmodulin and PI(3,4,5)P₃ cooperatively bind to the Itk ple...
2014-08-05 [Sci. Signal. 7(337) , ra74, (2014)] |
|
Social feeding in Caenorhabditis elegans is modulated by ant...
2015-05-01 [Neuropharmacology 92 , 56-62, (2015)] |
|
Multidirectional effects of calmodulin kinase II on transmit...
2013-01-01 [Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 154(3) , 316-9, (2013)] |