| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
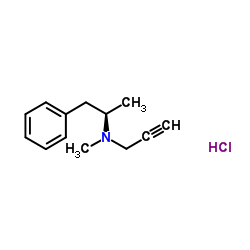 |
Selegiline HCl
CAS:14611-52-0 |
|
 |
E 250
CAS:2079-54-1 |
|
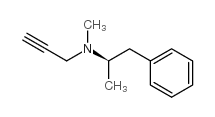 |
selegiline
CAS:14611-51-9 |