| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
(Z)-Chlorfenvinfos
CAS:470-90-6 |
|
 |
ovex
CAS:80-33-1 |
|
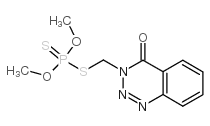 |
azinphos-methyl
CAS:86-50-0 |