| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
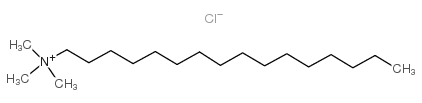 |
N-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride
CAS:112-02-7 |
|
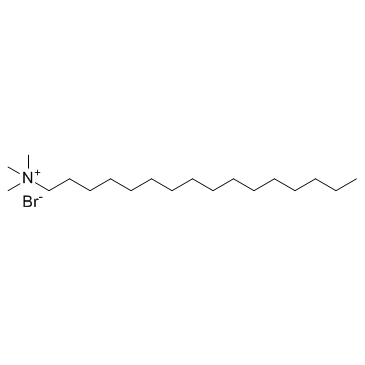 |
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
CAS:57-09-0 |
|
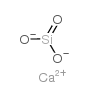 |
Calcium silicate
CAS:1344-95-2 |
|
 |
calcium silicate
CAS:10101-39-0 |
|
 |
Triosephosphate isomerase
CAS:9023-78-3 |
|
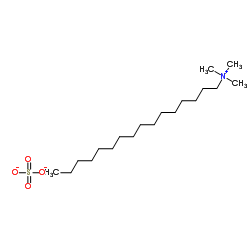 |
hexadecyl-trimethyl-ammonium sulfate
CAS:68214-07-3 |