Designing the ideal model for assessment of wound contamination after gunshot injuries: a comparative experimental study.
Constantin von See, Majeed Rana, Marcus Stoetzer, Horst Kokemueller, Martin Ruecker, Nils-Claudius Gellrich
Index: BMC Surg. 12 , 6, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Modern high-velocity projectiles produce temporary cavities and can thus cause extensive tissue destruction along the bullet path. It is still unclear whether gelatin blocks, which are used as a well-accepted tissue simulant, allow the effects of projectiles to be adequately investigated and how these effects are influenced by caliber size.Barium titanate particles were distributed throughout a test chamber for an assessment of wound contamination. We fired .22-caliber Magnum bullets first into gelatin blocks and then into porcine hind limbs placed behind the chamber. Two other types of bullets (.222-caliber bullets and 6.5 × 57 mm cartridges) were then shot into porcine hind limbs. Permanent and temporary wound cavities as well as the spatial distribution of barium titanate particles in relation to the bullet path were evaluated radiologically.A comparison of the gelatin blocks and hind limbs showed significant differences (p < 0.05) in the mean results for all parameters. There were significant differences between the bullets of different calibers in the depth to which barium titanate particles penetrated the porcine hind limbs. Almost no particles, however, were found at a penetration depth of 10 cm or more. By contrast, gas cavities were detected along the entire bullet path.Gelatin is only of limited value for evaluating the path of high-velocity projectiles and the contamination of wounds by exogenous particles. There is a direct relationship between the presence of gas cavities in the tissue along the bullet path and caliber size. These cavities, however, are only mildly contaminated by exogenous particles.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
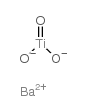 |
Barium titanate
CAS:12047-27-7 |
BaO3Ti |
|
Microwave absorption enhancement and electron microscopy cha...
2011-09-01 [Nanoscale 3(9) , 3860-7, (2011)] |
|
Ecotoxicological studies of micro- and nanosized barium tita...
2014-09-01 [Aquat. Toxicol. 154 , 58-70, (2014)] |
|
Interface engineered BaTiO₃/SrTiO₃ heterostructures with opt...
2012-11-01 [ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4(11) , 5761-5, (2012)] |
|
Numerical simulations of sonochemical production of BaTiO3 n...
2011-09-01 [Ultrason. Sonochem. 18(5) , 1211-7, (2011)] |
|
Nanostructured lead-free ferroelectric Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-BaTiO3...
2012-05-14 [Dalton Trans. 41(18) , 5643-52, (2012)] |