Immunosuppressive effects of silicon phthalocyanine photodynamic therapy.
J C Reddan, C Y Anderson, H Xu, S Hrabovsky, K Freye, R Fairchild, K A Tubesing, C A Elmets
Index: Photochem. Photobiol. 70(1) , 72-7, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to determine if silicon phthalocyanine 4 (Pc 4), a second-generation photosensitizer being evaluated for the photodynamic therapy (PDT) of solid tumors, was immunosuppressive. Mice treated with Pc 4 PDT 3 days before dinitrofluorobenzene sensitization showed significant suppression of their cell-mediated immune response when compared to mice that were not exposed to PDT. The response was dose dependent, required both Pc 4 and light and occurred at a skin site remote from that exposed to the laser. The immunosuppression could not be reversed by in vivo pre-treatment of mice with antibodies to tumor necrosis factor-alpha or interleukin-10. These results provide evidence that induction of cell-mediated immunity is suppressed after Pc 4 PDT. Strategies that prevent PDT-mediated immunosuppression may therefore enhance the efficacy of this therapeutic modality.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
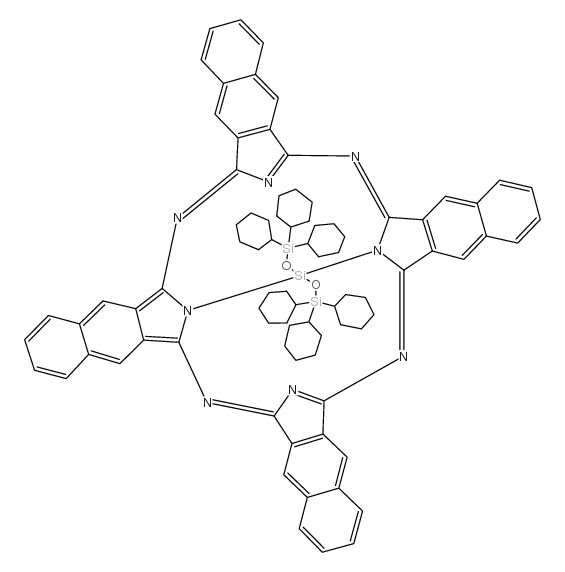 |
bis(trihexylsiloxy)silicon 2,3-naph- thalocyanine
CAS:92396-88-8 |
C84H90N8O2Si3 |
|
Phthalocyanine photodynamic therapy: disparate effects of ph...
1997-05-01 [Photochem. Photobiol. 65(5) , 895-901, (1997)] |
|
Plasma pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution in CD2F1 mic...
1999-01-01 [Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 44(4) , 283-94, (1999)] |
|
Silicon phthalocyanine Pc 4 and red light causes apoptosis i...
1997-03-01 [Photochem. Photobiol. 65(3) , 456-60, (1997)] |
|
Photodynamic activities of silicon phthalocyanines against a...
1999-01-01 [J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 48(1) , 48-56, (1999)] |
|
Structure-activity and mechanism studies on silicon phthaloc...
1997-08-01 [Photochem. Photobiol. 66(2) , 282-7, (1997)] |