Formation of embryogenic cell clumps from carrot epidermal cells is suppressed by 5-azacytidine, a DNA methylation inhibitor.
Nozomi Yamamoto, Hatsumi Kobayashi, Takashi Togashi, Yukiko Mori, Koji Kikuchi, Kyoko Kuriyama, Yoshihiko Tokuji
Index: J. Plant Physiol. 162(1) , 47-54, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Using a direct somatic embryogenesis system in carrot, we examined the role of DNA methylation in the change of cellular differentiation state, from somatic to embryogenic. 5-Azacytidine (aza-C), an inhibitor of DNA methylation suppressed the formation of embryogenic cell clumps from epidermal carrot cells. Aza-C also downregulated the expression of DcLEC1c, a LEC1-like embryonic gene in carrot, during morphogenesis of embryos. A carrot DNA methyltransferase gene, Met1-5 was expressed transiently after the induction of somatic embryogenesis by 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), before the formation of embryogenic cell clumps. These findings suggested the significance of DNA methylation in acquiring the embryogenic competence in somatic cells in carrot.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
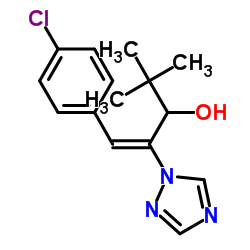 |
Prunit
CAS:83657-22-1 |
C15H18ClN3O |
|
Improved biological effects of uniconazole using porous holl...
2012-03-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 68(3) , 437-43, (2012)] |
|
Enantiomeric resolution and growth-retardant activity in ric...
2012-01-11 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(1) , 160-4, (2012)] |
|
Involvement of gibberellin in tracheary element differentiat...
2006-09-01 [Protoplasma 228(4) , 179-87, (2006)] |
|
Plants with increased expression of ent-kaurene oxidase are ...
2005-02-01 [Plant Cell Physiol. 46(2) , 284-91, (2005)] |
|
Metabolism of uniconazole-P in water-sediment systems under ...
2006-02-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 25(2) , 310-6, (2006)] |