Interaction of 4-aminopyridine with [3H]phencyclidine receptors in rat brain homogenates.
W S Lai, E E el-Fakahany, Wi S. Lai, Esam E. El-Fakahany
Index: Neurosci. Lett. 67(1) , 87-91, (1986)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effect of 4-aminopyridine and its analogs on the specific binding of [3H]phencyclidine was investigated in rat brain homogenates. 4-Aminopyridine (4-AP) and 3,4-diaminopyridine displaced [3H]phencyclidine binding, while 3-aminopyridine was without effect. The concentrations of 4-AP required for inhibition of binding increased with increasing the ligand concentration, and the resultant Dixon plots indicated a competitive type of interaction. However, 4-AP also accelerated the dissociation rate of the ligand-receptor complex, suggesting that the effect of 4-AP on phencyclidine receptors in the brain might not be purely competitive.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
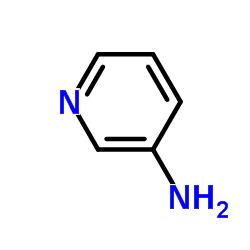 |
3-Aminopyridine
CAS:462-08-8 |
C5H6N2 |
|
Anharmonic vibrational analysis of 3,4-diaminopyridine and 3...
2010-09-01 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 76(5) , 502-12, (2010)] |
|
Evaluation of electrophilic heteroaromatic substitution: syn...
2012-10-05 [J. Org. Chem. 77(19) , 8492-500, (2012)] |
|
The significance of the temporal bond polarizabilty relaxati...
2008-12-15 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 71(4) , 1588-93, (2008)] |
|
Surface complexation modeling of the sorption of 2-, 3-, and...
2005-04-15 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 284(2) , 383-92, (2005)] |
|
Two salts of 5-sulfosalicylic acid and 3-aminopyridine.
2007-11-01 [Acta Crystallogr. C 63(Pt 11) , o667-70, (2007)] |