PETN ignition experiments and models.
Michael L Hobbs, William B Wente, Michael J Kaneshige
Index: J. Phys. Chem. A 114(16) , 5306-19, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Ignition experiments from various sources, including our own laboratory, have been used to develop a simple ignition model for pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN). The experiments consist of differential thermal analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, differential scanning calorimetry, beaker tests, one-dimensional time to explosion tests, Sandia's instrumented thermal ignition tests (SITI), and thermal ignition of nonelectrical detonators. The model developed using this data consists of a one-step, first-order, pressure-independent mechanism used to predict pressure, temperature, and time to ignition for various configurations. The model was used to assess the state of the degraded PETN at the onset of ignition. We propose that cookoff violence for PETN can be correlated with the extent of reaction at the onset of ignition. This hypothesis was tested by evaluating metal deformation produced from detonators encased in copper as well as comparing postignition photos of the SITI experiments.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
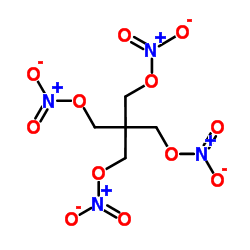 |
Pentaerithrityl tetranitrate
CAS:78-11-5 |
C5H8N4O12 |
|
Organic nitrates differentially modulate circulating endothe...
2011-08-15 [Antioxid. Redox Signal. 15(4) , 925-31, (2011)] |
|
Magnetic field-cycling NMR and14N,17O quadrupole resonance i...
2010-01-01 [J. Magn. Reson. 204(1) , 139-44, (2010)] |
|
Terahertz normal mode relaxation in pentaerythritol tetranit...
2011-01-07 [J. Chem. Phys. 134(1) , 014513, (2011)] |
|
Embossing of organic thin films using a surfactant assisted ...
2012-12-01 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 387(1) , 175-9, (2012)] |
|
Improved accuracy in high-temperature conversion elemental a...
2012-03-15 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 26(5) , 554-62, (2012)] |