| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
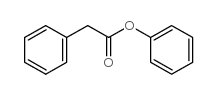 |
phenyl phenylacetate
CAS:722-01-0 |
L Haagen, A Brock
Index: Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 30(7) , 391-5, (1992)
Full Text: HTML
A new method for phenotyping human serum arylesterase (EC 3.1.1.2) is described and evaluated. The aromatic esters, phenyl acetate and 4-nitrophenyl acetate, were compared as substrates for spectrophotometric measurement of arylesterase activity. A method for arylesterase phenotyping, based upon inhibition of the enzymatic hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl acetate by phenyl acetate, was developed. The method was applied to serum samples from 158 blood donors and showed a distinct separation of the three phenotypes defined by a reference method based on the ratio of paraoxonase activity to arylesterase activity using paraoxon and phenyl acetate as substrates. The method was adapted to a Cobas-Fara centrifugal analyser.
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
phenyl phenylacetate
CAS:722-01-0 |
C14H12O2 |
|
Kinetics of substrate hydrolysis and inhibition by mipafox o...
1986-06-01 [Biochem. J. 236(2) , 503-7, (1986)] |
|
Photochemistry of phenyl phenylacetates adsorbed on pentasil...
[J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. II 7 , 1319-22, (1997)] |
|
Molecular rearrangements. Part XX. Thermolysis of carboxylic...
[Can. J. Chem. 61(7) , 1532-35, (1983)] |
|
Selectivity in the photo-Fries reaction of phenyl phenylacet...
[Tetrahedron Lett. 40(1) , 127-30, (1999)] |
Home | MSDS/SDS Database Search | Journals | Product Classification | Biologically Active Compounds | Selling Leads | About Us | Disclaimer
Copyright © 2024 ChemSrc All Rights Reserved