| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
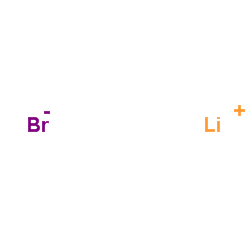 |
Lithium bromide
CAS:7550-35-8 |
|
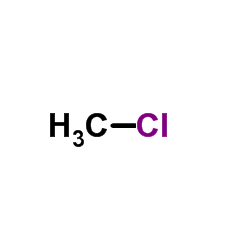 |
Chloromethane
CAS:74-87-3 |
|
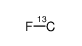 |
fluoromethane-13c
CAS:20666-44-8 |