| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
1,1'-Dioctadecyl-3,3,3',3'-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate
CAS:41085-99-8 |
|
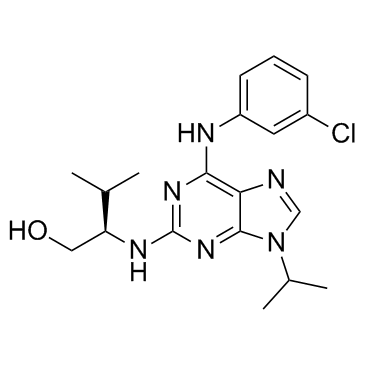 |
Purvalanol A
CAS:212844-53-6 |