Oxidative decarboxylation of 3,4-dihydroxymandelic acid to 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde: electrochemical and HPLC analysis of the reaction mechanism.
T H Czapla, M R Claeys, T D Morgan, K J Kramer, T L Hopkins, M D Hawley
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1077(3) , 400-6, (1991)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Cyclic voltammetric and chronoamperometric data are consistent with a process in which 3,4-dihydroxymandelic acid (DOMA) is oxidized initially in a two-electron step to its corresponding o-benzoquinone. This species is unstable and undergoes the rate-determining loss of CO2 (k = 1.6 s-1 at pH 6 and 25 degrees C) to give an unobserved p-benzoquinone methide intermediate that rapidly isomerizes to 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (DOBAL), DOBAL is also electroactive at the applied potential and is oxidized in a two-electron step to 4-formyl-1,2-benzoquinone. Subsequent reactions of 4-formyl-1,2-benzoquinone include the oxidation of unreacted DOMA and the hydration of its aldehyde functional group. Oxidation of DOMA directly to its p-benzoquinone methide apparently does not occur. Derivatives of mandelic acid (e.g., 4-hydroxymandelic acid) that are expected to give only their corresponding p-benzoquinone methides upon oxidation afford redox behavior that differs distinctly from that for DOMA.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
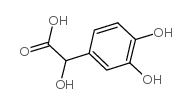 |
3,4-Dihydroxymandelic acid
CAS:14883-87-5 |
C8H8O5 |
|
Lipophilicity of amine neurotransmitter precursors, metaboli...
2014-10-01 [J. Chromatogr. Sci. 52(9) , 1095-103, (2014)] |
|
Further study on the use of uncharged beta-cyclodextrin poly...
1995-08-01 [Electrophoresis 16(8) , 1505-9, (1995)] |
|
Mechanistic studies on tyrosinase-catalysed oxidative decarb...
1992-01-15 [Biochem. J. 281 ( Pt 2) , 353-7, (1992)] |
|
Chemical and enzymic oxidation by tyrosinase of 3,4-dihydrox...
1988-12-01 [Biochem. J. 256(2) , 681-4, (1988)] |
|
3,4-Dihydroxymandelic acid, a noradrenalin metabolite with p...
2002-10-09 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(21) , 5897-902, (2002)] |