| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
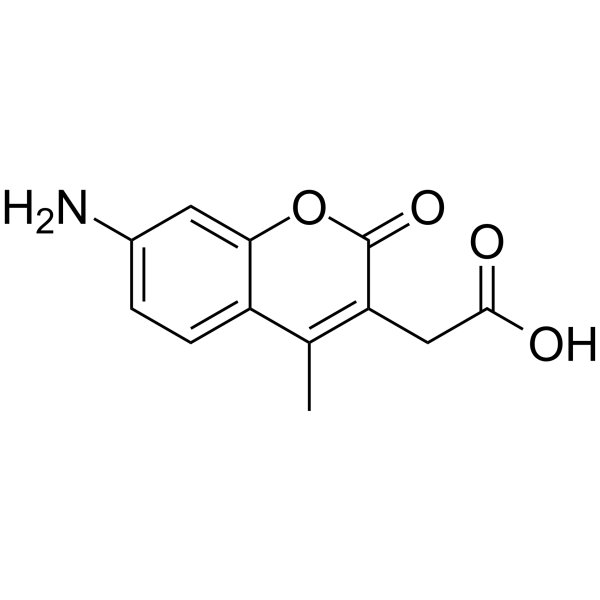 |
7-Amino-4-methylcoumarin-3-acetic acid
CAS:106562-32-7 |
|
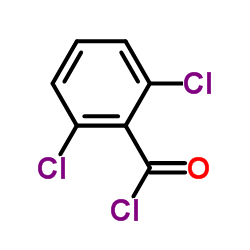 |
2,6-Dichlorobenzoyl chloride
CAS:4659-45-4 |