| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
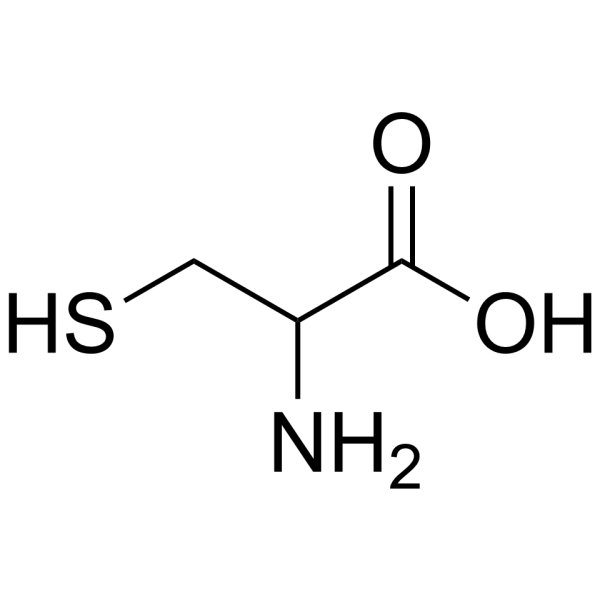 |
DL-CYSTEINE (1-13C)
CAS:3374-22-9 |
|
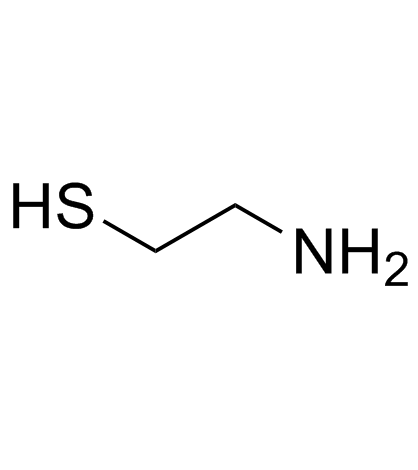 |
2-Aminoethanethiol
CAS:60-23-1 |
|
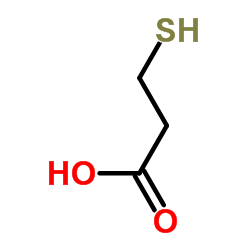 |
3-Mercaptopropionic acid
CAS:107-96-0 |
|
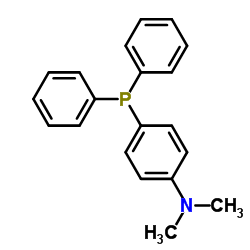 |
4-(Dimethylamino)phenyldiphenylphosphine
CAS:739-58-2 |