| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
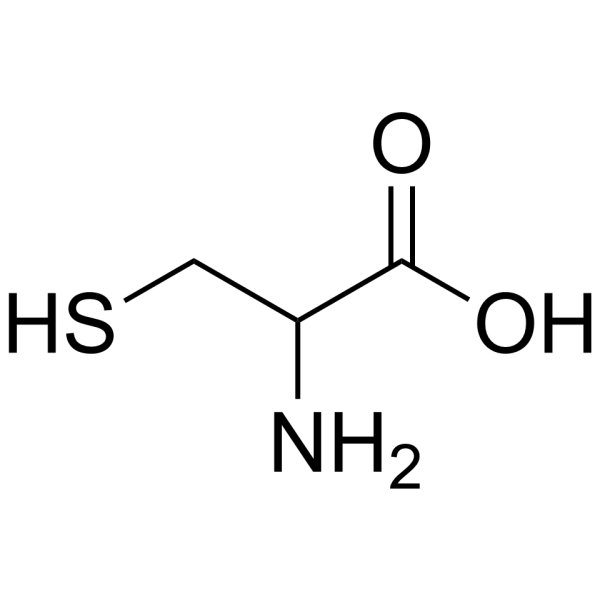 |
DL-CYSTEINE (1-13C)
CAS:3374-22-9 |
|
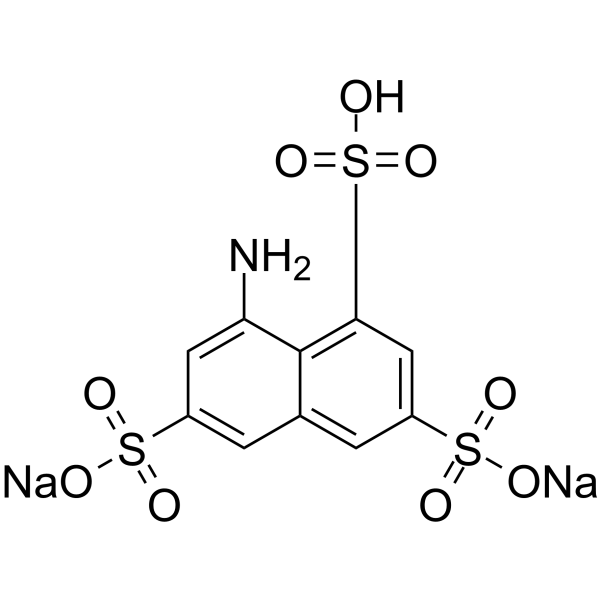 |
8-Aminonaphthalene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid disodium salt
CAS:5398-34-5 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
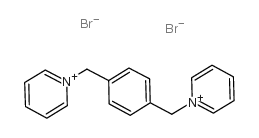 |
dpx
CAS:14208-10-7 |