Selective electrochemical discrimination between dopamine and phenethylamine-derived psychotropic drugs using electrodes modified with an acyclic receptor containing two terminal 3-alkoxy-5-nitroindazole rings.
Antonio Doménech, Pilar Navarro, Vicente J Arán, Beatriz Muro, Noemí Montoya, Enrique García-España
Index: Analyst 135(6) , 1449-55, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Electrochemical discrimination between dopamine and psychotropic drugs which have in common a skeletal structure of phenethylamine, can be obtained using acyclic receptors L(1) and L(2), containing two terminal 3-alkoxy-5-nitroindazole rings. Upon attachment to graphite electrodes, L(1) and L(2) exhibit a well-defined, essentially reversible solid state electrochemistry in contact with aqueous media, based on electrolyte-assisted reduction processes involving successive cation and anion insertion/binding. As a result, a distinctive, essentially Nernstian electrochemical response is obtained for phenethylammonium ions of methamphetamine (METH), p-methoxyamphetamine (PMA), amphetamine (AMPH), mescaline (MES), homoveratrylamine (HOM), phenethylamine (PEA) and dopamine (DA) in aqueous media.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
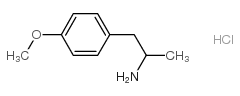 |
pma hydrochloride
CAS:52740-56-4 |
C10H16ClNO |
|
Studies on distribution and metabolism of para-methoxymetham...
2009-05-02 [Toxicology 259(1-2) , 61-8, (2009)] |
|
The effects of co-administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymetham...
2007-04-25 [Neuroscience 146(1) , 321-9, (2007)] |
|
Effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, 'Ecstasy...
2005-04-11 [Brain Res. 1041(1) , 48-55, (2005)] |
|
Repeated administration of the substituted amphetamine p-met...
2006-09-28 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 546(1-3) , 74-81, (2006)] |
|
Potentiation of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine-induced 5-...
2007-10-01 [Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 34(10) , 1051-7, (2007)] |