| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Selenium
CAS:7782-49-2 |
|
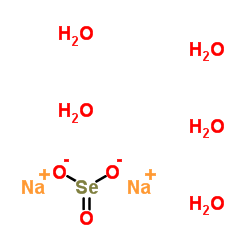 |
Sodium selenite hydrate (2:1:5)
CAS:26970-82-1 |
|
 |
Sodium selenite
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
 |
sodium,hydrogen selenite
CAS:7782-82-3 |