C-terminal N-alkylated peptide amides resulting from the linker decomposition of the Rink amide resin: a new cleavage mixture prevents their formation.
Panagiotis Stathopoulos, Serafim Papas, Vassilios Tsikaris
Index: J. Pept. Sci. 12(3) , 227-32, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Decomposition of the resin linkers during TFA cleavage of the peptides in the Fmoc strategy leads to alkylation of sensitive amino acids. The C-terminal amide alkylation, reported for the first time, is shown to be a major problem in peptide amides synthesized on the Rink amide resin. This side reaction occurs as a result of the Rink amide linker decomposition under TFA treatment of the peptide resin. The use of 1,3-dimethoxybenzene in a cleavage cocktail prevents almost quantitatively formation of C-terminal N-alkylated peptide amides. Oxidized by-product in the tested Cys- and Met-containing peptides were not observed, even if thiols were not used in the cleavage mixture.Copyright (c) 2005 European Peptide Society and John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
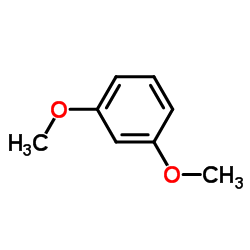 |
1,3-Dimethoxybenzene
CAS:151-10-0 |
C8H10O2 |
|
Rotamers of o- and m-dimethoxybenzenes studied by mass-analy...
2010-10-28 [J. Phys. Chem. A 114(42) , 11144-52, (2010)] |
|
Stereoselective glycosylations using oxathiane spiroketal gl...
2012-02-01 [Carbohydr. Res. 348 , 6-13, (2012)] |
|
Solvation of dichlorocarbene: complexation with aryl ethers.
2010-01-14 [J. Phys. Chem. A 114(1) , 209-17, (2010)] |
|
Decrease in glucose oxidation in isolated brown fat cells fr...
1981-01-01 [Gen. Pharmacol. 12(1) , 47-50, (1981)] |
|
Optimization of the solid-phase microextraction method in th...
2006-02-01 [J. Sep. Sci. 29(2) , 236-41, (2006)] |